
Mid-Slope Attenuators
Mid-slope attenuators are hybrid rockfall protection systems positioned partway down a slope to intercept falling rocks before they gain full momentum, reducing energy and enabling more efficient catchment at the base.
Understanding Mid-Slope Attenuators
Mid-slope attenuators combine the interception capability of draped mesh with the energy-absorbing technology of flexible barriers. By catching rocks mid-slope—before they reach maximum velocity—attenuators dramatically reduce the energy that must be absorbed by base-of-slope barriers or catchment areas.
This strategic positioning allows engineers to specify lower-capacity (less expensive) barriers at the base, reduce catchment ditch dimensions, and protect areas where full-height barriers aren't feasible. Attenuators are particularly effective on tall slopes where rocks would otherwise gain dangerous momentum.
This technique is used in our services for:

Typical Applications
How It Works
Our proven methodology ensures consistent, high-quality results for every installation.
Rockfall Trajectory Analysis
Model rockfall paths using 2D or 3D simulation software to identify optimal interception points. Analysis determines rock velocities, bounce heights, and energy levels at various slope positions to size the attenuator system appropriately.
Anchor System Design
Design anchor patterns for top support, intermediate suspension points, and lateral restraint. Anchors must resist both static mesh weight and dynamic impact loads during rockfall events.
Top Anchor Installation
Install rock bolts or cable anchors at the top attachment line using rope access or mechanical drilling. Anchors are load-tested to verify capacity before mesh attachment.
Mesh Panel Deployment
Deploy wire rope nets or ring net panels from top anchors, incorporating energy-absorbing brake elements at connection points. Panels are joined with shackles or ferrules to create continuous coverage.
Energy Absorber Installation
Install compression brakes, friction brakes, or ring-net deformation elements that absorb impact energy by controlled deformation. These elements are the key to attenuator performance.
Base Termination
Terminate the bottom edge with ground anchors for full containment, or allow controlled release toward a lower catchment system. Termination method depends on overall rockfall management strategy.
Key Advantages
Energy Reduction Strategy
By intercepting rocks at 30-50% of slope height, attenuators can reduce impact energy by 50-70%, allowing significant savings on downstream protection systems.
Cost-Effective for Tall Slopes
On slopes over 200 feet, mid-slope attenuators often cost less than upgrading base barriers to handle full-energy impacts or installing full-coverage draped mesh.
Flexible System Integration
Attenuators integrate with existing barriers, ditches, and mesh systems. They can be added to improve performance of under-capacity existing systems.
Reduced Maintenance Burden
By reducing impact energies at base barriers, attenuators extend barrier life and reduce the frequency of post-event repairs and debris clearing.
Adaptable to Site Constraints
Where catchment areas are constrained by roads, rails, or property lines, attenuators reduce bounce heights and rollout distances, keeping rocks within available catchment.
Technical Considerations
Soil/Rock Conditions
Anchors require competent rock or soil for adequate pullout resistance. Weathered or fractured rock may require longer anchors, grouted installations, or multiple anchor points to distribute loads.
Groundwater
Drainage behind attenuator panels prevents ice loading in cold climates. Weep paths through the system allow water to drain without building pressure on anchors.
Load Capacity
Attenuator capacity is determined by mesh strength, energy absorber capacity, and anchor pullout resistance. All components must be sized for the design impact energy based on trajectory analysis.
Spacing
Anchor spacing depends on mesh type, span capability, and design loads. Closer spacing required for higher energy systems or weaker anchor conditions.
Installation Method
Installation typically requires rope access crews for anchor drilling and mesh deployment on steep terrain. Helicopter support may be needed for material delivery to remote locations.
Equipment Used
- Rope access drilling equipment
- Hydraulic rock drills
- Helicopter for material delivery (remote sites)
- Tensioning equipment for cable anchors
- Rigging equipment for mesh deployment
Limitations
- Requires suitable anchor locations mid-slope
- Not effective where rocks originate below attenuator line
- Periodic inspection and maintenance required
- May need debris clearing after significant events
- Ice accumulation possible in cold climates
Technical Specifications
System Variations
Suspended Attenuator
Mesh panels hung from top anchors with free-hanging bottom edge, allowing rocks to pass beneath while reducing energy through mesh deflection and brake element activation.
Best For:
- High bounce-height zones
- Areas requiring rock passage to lower catchment
- Aesthetic-sensitive locations
Anchored Attenuator
Full perimeter anchoring with top, bottom, and side attachments creating a contained interception zone. Higher capacity but requires anchor access at all attachment points.
Best For:
- Maximum containment required
- Lower slopes with base access
- Critical infrastructure protection
Multi-Tier Attenuator System
Multiple attenuator lines positioned at different slope heights for staged energy reduction on very tall slopes. Each tier reduces energy before rocks reach the next level.
Best For:
- Slopes exceeding 500 feet
- Mining highwalls
- Multi-bench configurations
Hybrid Attenuator-Barrier
Attenuator mesh integrated with rigid barrier posts and energy-absorbing elements for combined interception and full containment capability.
Best For:
- Zero-tolerance rockfall zones
- Areas with no downstream catchment
- Critical facility protection
Integration With Other Systems
Rockfall Barriers
Attenuators reduce impact energy reaching base barriers, enabling use of lower-capacity systems and extending barrier service life.
Learn More
Draped Mesh Systems
Attenuators can supplement partial draped coverage or provide additional protection below draped zones where rocks may emerge.
Learn More
Rock Bolting
Rock bolts provide anchor points for attenuator suspension and may stabilize source areas above the attenuator line.
Learn More
Cable Anchors
High-capacity cable anchors provide the pullout resistance needed for attenuator systems subjected to large impact loads.
Learn MoreExample Project Types
- Highway rockfall mitigation
- Railroad corridor protection
- Mining highwall safety
- Ski resort terrain management
- Residential development protection
- Infrastructure corridor protection
- Dam and spillway approaches
- Recreational area hazard management
Why Choose Rock Supremacy for Mid-Slope Attenuators
Trajectory Analysis Expertise
Our engineers use advanced rockfall simulation to identify optimal attenuator positions that maximize energy reduction and minimize system cost.
Rope Access Installation
Trained crews install attenuators in terrain where conventional equipment cannot operate, ensuring quality work on the steepest slopes.
Integrated System Design
We design attenuators as part of comprehensive rockfall management systems, coordinating with barriers, mesh, and catchment for optimal overall performance.
Certified Products
We install ETAG 027-certified attenuator systems with documented energy capacities and proven performance in testing and field applications.
Maintenance Programs
Our inspection and maintenance services keep attenuator systems performing at design capacity throughout their service life.
Our Work
See how we've applied this technique and others to solve real-world geotechnical challenges.
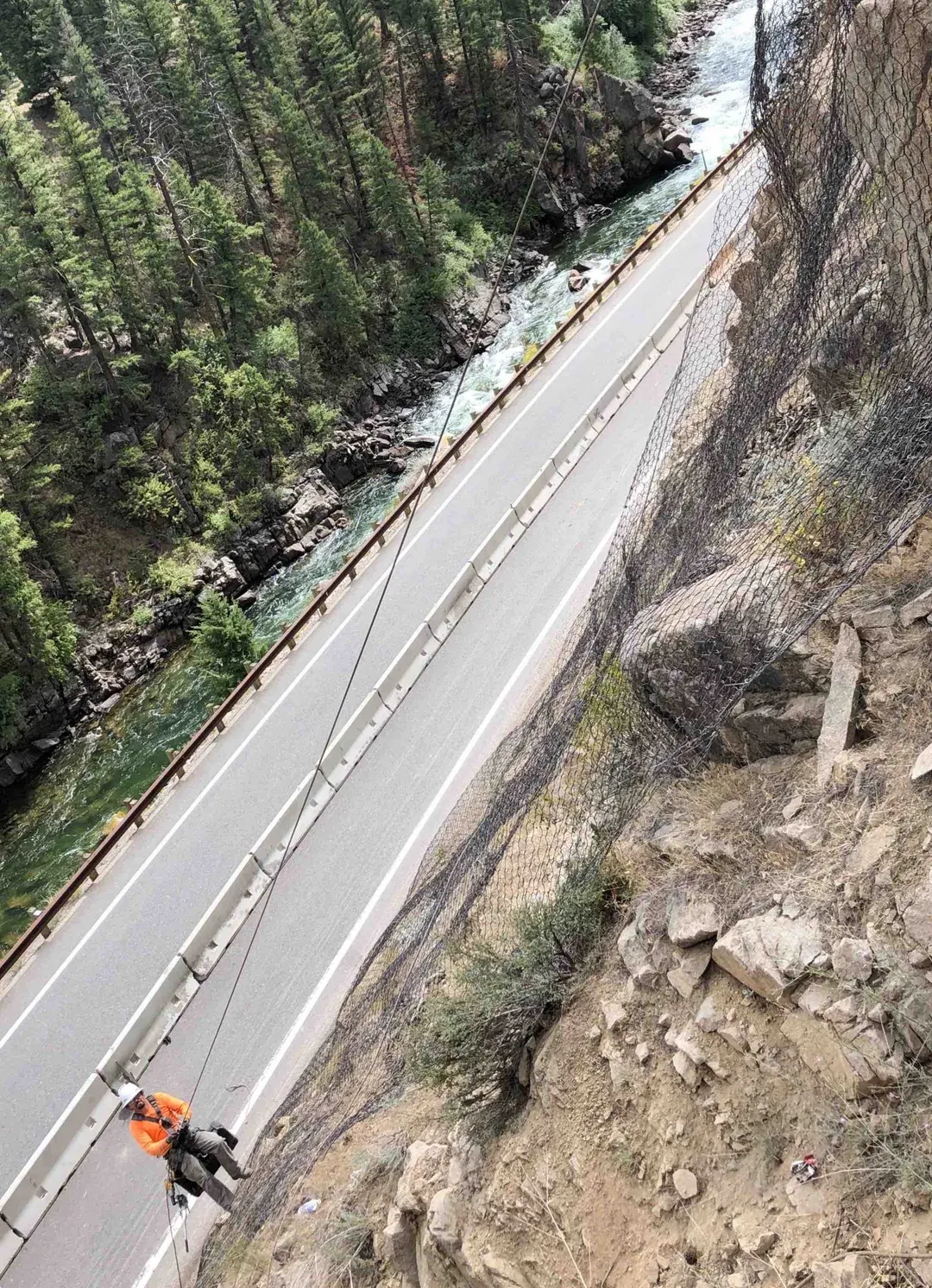

I-70 Corridor Stabilization
Installed 50,000 sq ft of high-tensile mesh and performed extensive scaling after a major weather event.
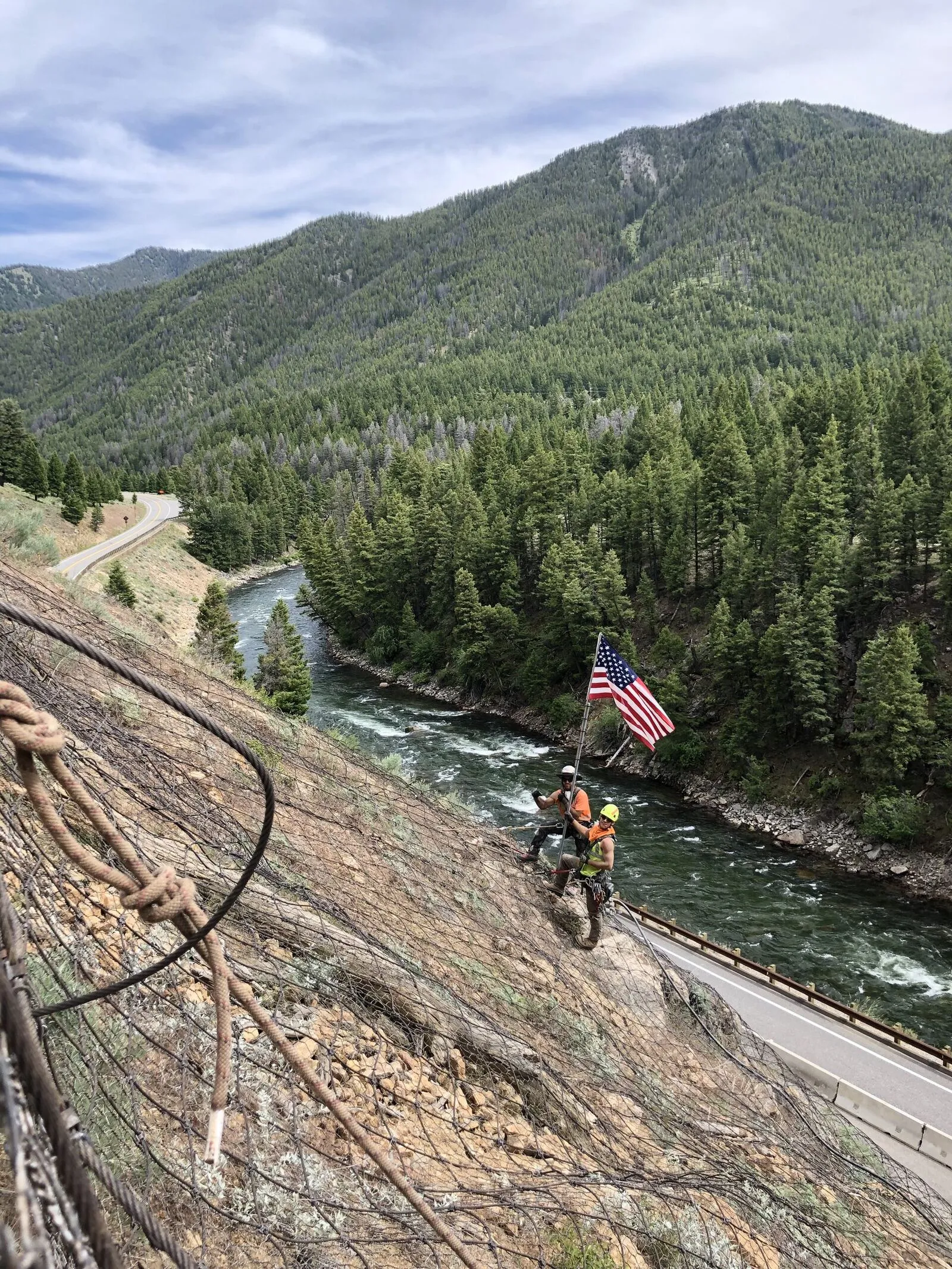

Ketchum-Challis Highway Scaling
Large-scale rock scaling and mesh installation along 3 miles of Highway 75 through the Sawtooth Mountains.
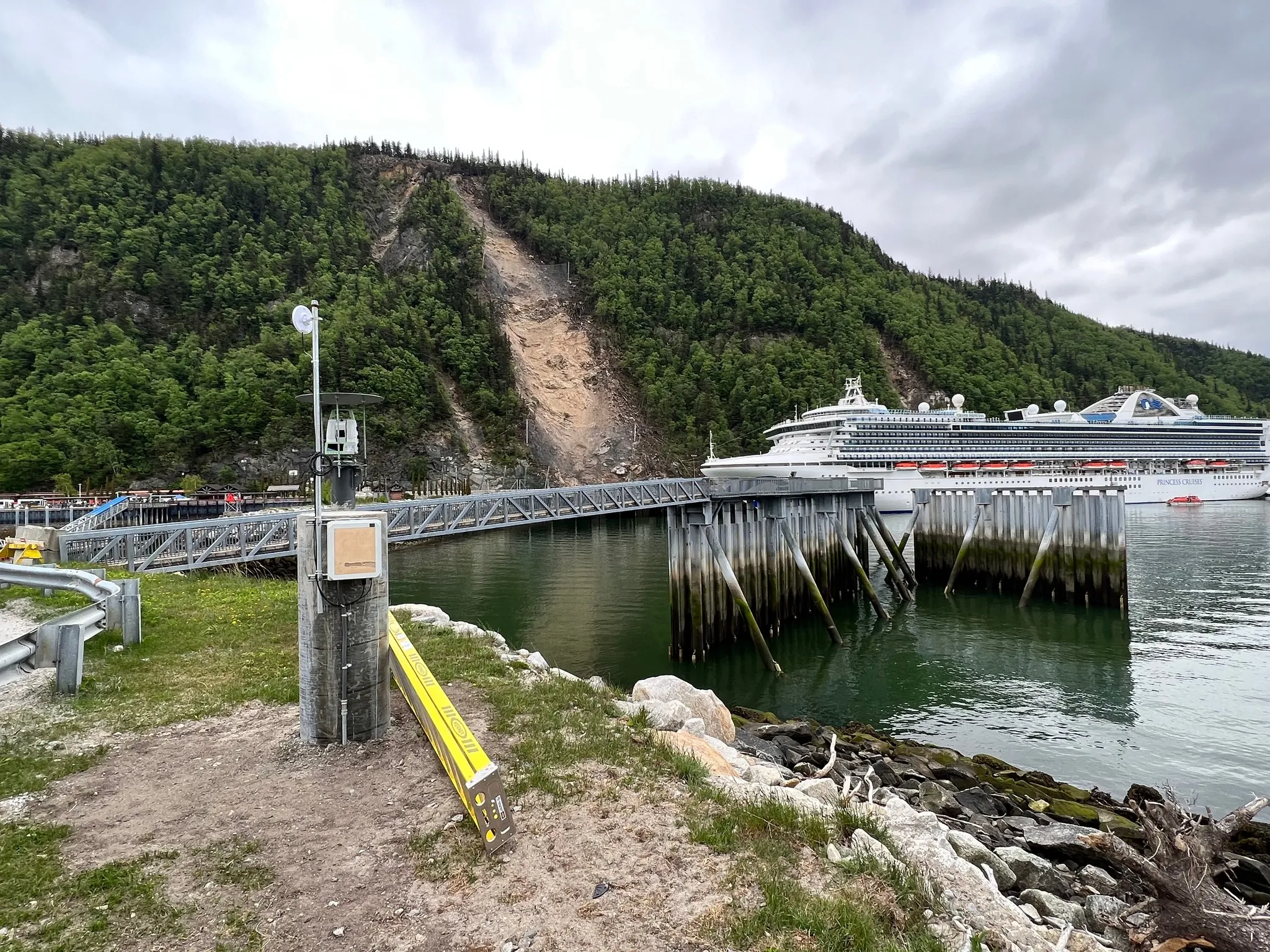

Skagway Port Rockfall Protection
Comprehensive rockfall mitigation protecting Alaska's busiest cruise port from an 800-foot active slope, completed in a single winter season before the 2023 tourism season.
Mid-Slope Attenuators FAQ
Client Testimonials
Trusted by DOTs, engineering firms, and property owners nationwide.
Deploy Us
Ready to discuss your project? Our team is standing by to assess your site conditions and develop a custom solution using Mid-Slope Attenuators and other proven techniques.
Emergency (24/7)
(541) 383-7625Bidding & Estimates
Info@RockSupremacy.comHeadquarters
Licensed in CO, UT, WY, ID, MT, CA, WA, OR, TN, VA
Request Consultation
Related Techniques
Explore other engineering methods we use to deliver comprehensive geotechnical solutions.
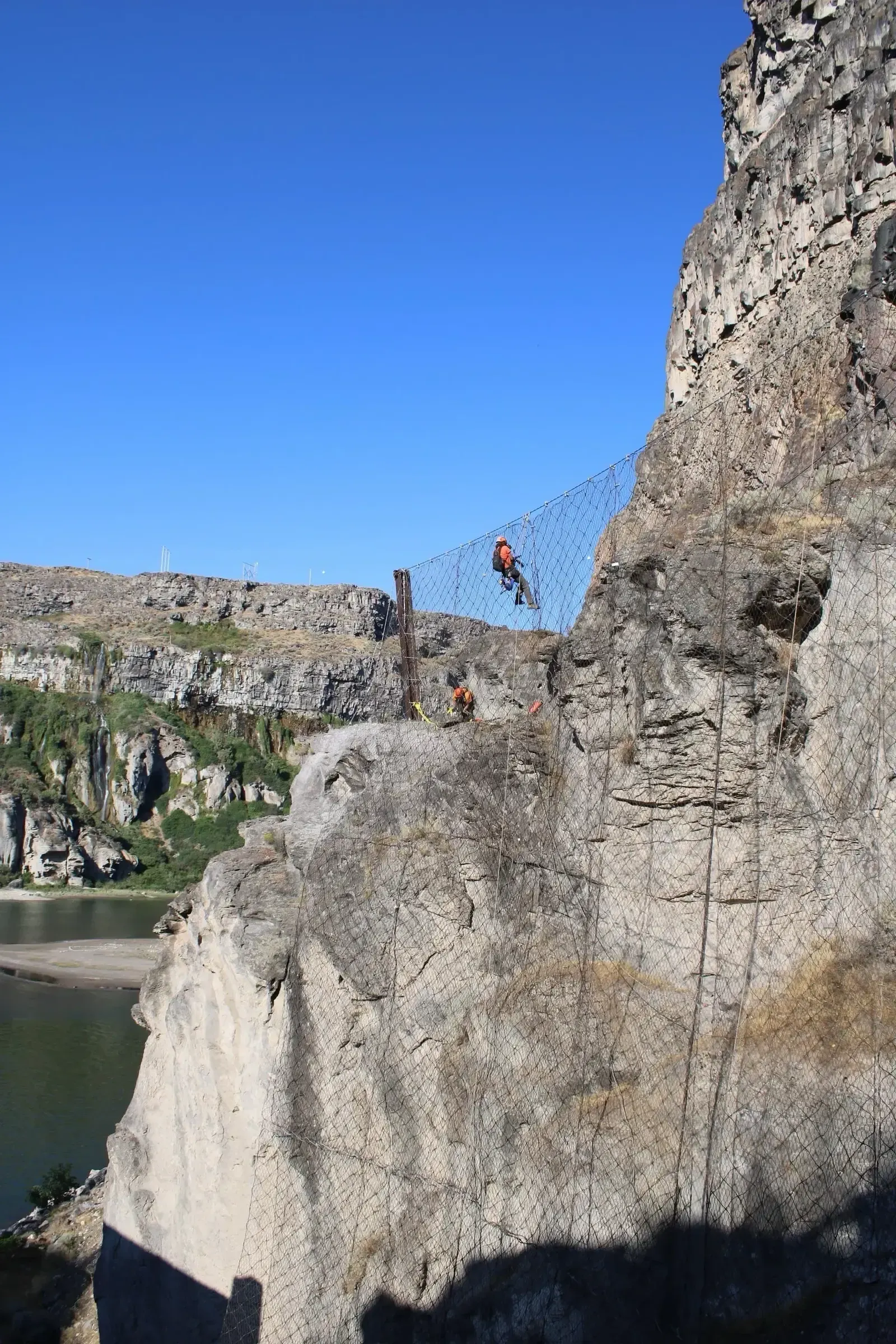

Draped Mesh Systems
Draped mesh systems control loose rockfall by capturing debris and guiding it downslope to a safe catchment area. Unlike pinned mesh, draped systems are not rigidly attached to the entire slope—allowing them to manage high volumes of material efficiently.
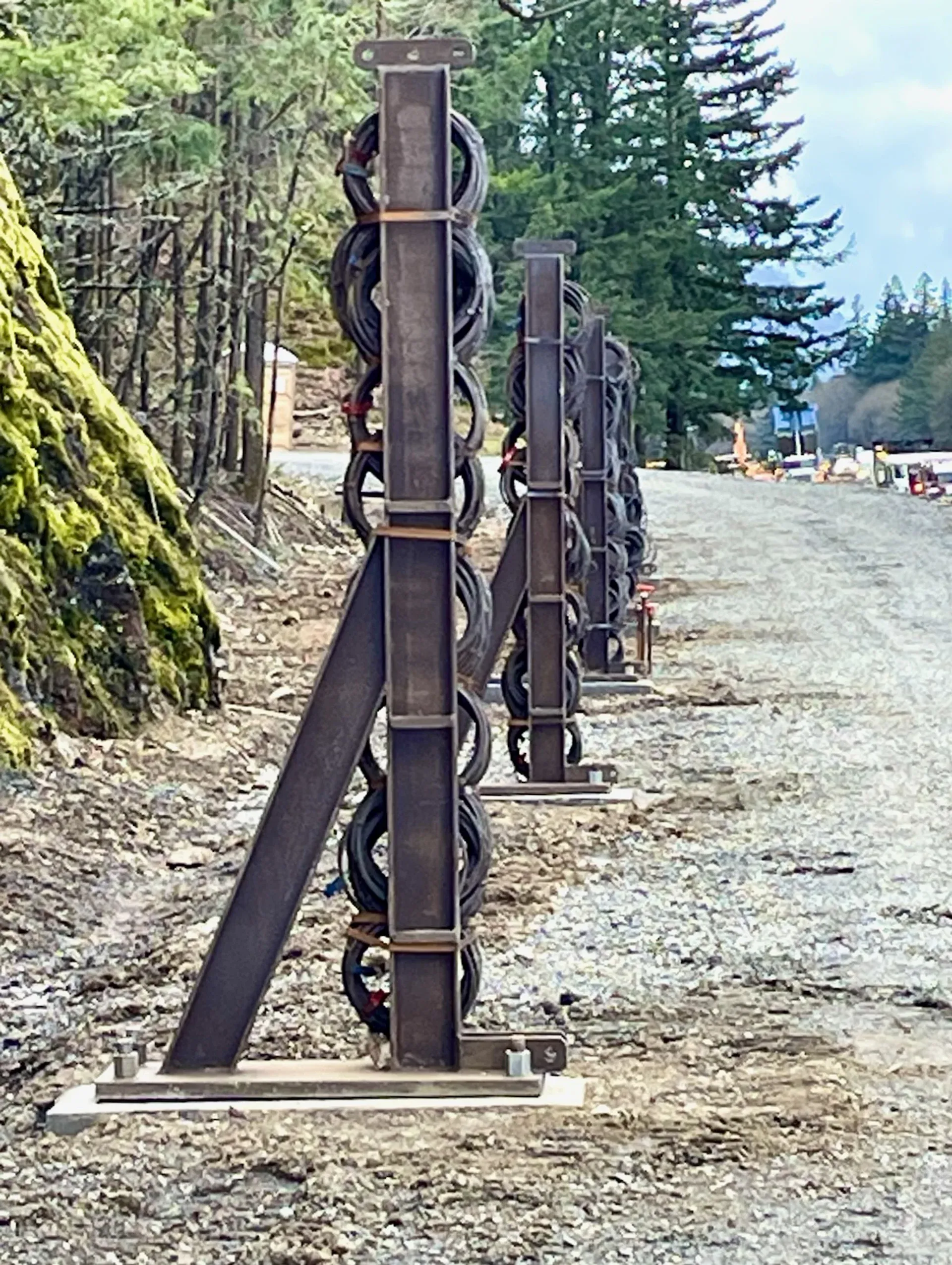

High-Energy Rockfall Barriers
High-energy barriers provide advanced rockfall protection for slopes where large blocks, high drop heights, or extreme impact forces exceed conventional barrier capacity. These systems absorb up to 10,000 kJ through flexible ring nets, energy-dissipating brakes, and engineered post foundations.
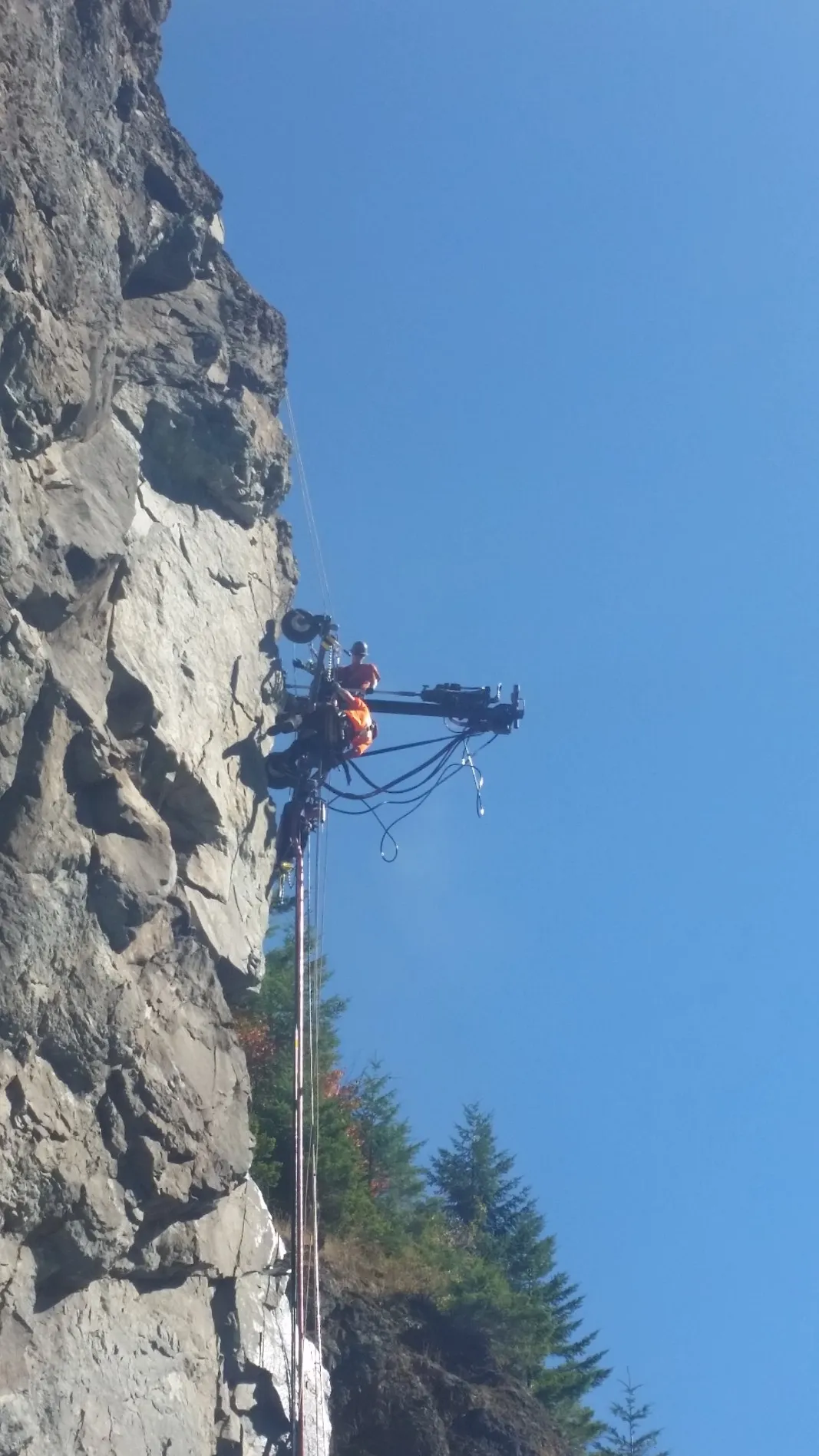


Rock Bolting
Rock bolting stabilizes fractured, jointed, or unstable rock masses by anchoring steel bars deep into competent rock. By tying loose blocks back to stable substrate, rock bolts improve the overall strength and cohesion of slopes, cuts, tunnels, and vertical faces.


Rockfall Barriers & Fences
Engineered catch systems that intercept falling rock or debris before it reaches roadways, railways, or infrastructure. These high-energy systems absorb and dissipate impact energy safely through deformable components.